The Margin Level in forex trading represents the ratio of your Equity to Used Margin, expressed as a percentage (%). It is a crucial metric that every trader should grasp to manage their positions effectively.
Knowing your Margin Level is essential as it indicates the amount of available funds you have for new trades. It reflects the health of your account and influences your trading decisions.
The rule of thumb is simple: the higher your Margin Level, the more Free Margin you possess for trading activities. Conversely, a lower Margin Level implies limited Free Margin, which can lead to unfavorable outcomes like Margin Calls or Stop Outs.
To calculate your Margin Level, use the following formula:
Your trading platform will automatically compute and display this metric for you. When you have no active trades, your Margin Level will be at ZERO, indicating no available funds for additional positions.
Margin Level plays a vital role in forex trading, influencing your ability to initiate new trades. Forex brokers utilize this indicator to evaluate your account’s readiness for further trading activities.
Understanding and monitoring this metric can help you make informed decisions, manage risk effectively, and optimize your trading strategies for better outcomes in the dynamic forex market.
Are you familiar with the concept of Margin Level in trading? Understanding this key aspect is crucial for managing your positions effectively and making informed decisions. Let’s delve into how Margin Level influences your trading activities.
What is Margin Level?
Margin Level is a vital parameter that dictates the amount of funds you need in your trading account to open new positions. Various brokers have different Margin Level limits, typically set around 100%. When your Equity equals or falls below the Used Margin, you won’t be able to initiate new trades until you address this discrepancy.
Practical Example
Imagine you’re eager to open a long position on USD/JPY with 1 mini lot. Let’s break down the process step by step to grasp the calculations involved.
Step 1: Calculate Required Margin
- Account Balance: $1 000
- Position Size: 1 mini lot (10 000 units)
- Margin Requirement: 4%
To determine the Required Margin for this trade, consider the Notional Value of the position:
Therefore, the calculation for Required Margin is:
If your trading account is denominated in USD, you’d need $400 as the Required Margin to open this position successfully.
Understanding Forex Trading: Calculating Margin Level
Step 2: Calculating Used Margin
When you have only one open trade, the Used Margin is the same as the Required Margin for that trade.
Step 3: Calculating Equity
Imagine your trade has broken even, with no floating profit or loss. To find your Equity:
Equity = Account Balance + Floating Profits (or Losses)
Therefore, your account’s Equity stands at $1 000.
Step 4: Calculating Margin Level
Once Equity is determined, you can calculate the Margin Level:
Margin Level = (Equity / Margin) x 100%
This results in a Margin Level of 250%.
Having a Margin Level of 100% or lower may restrict your ability to open new trades on many trading platforms.
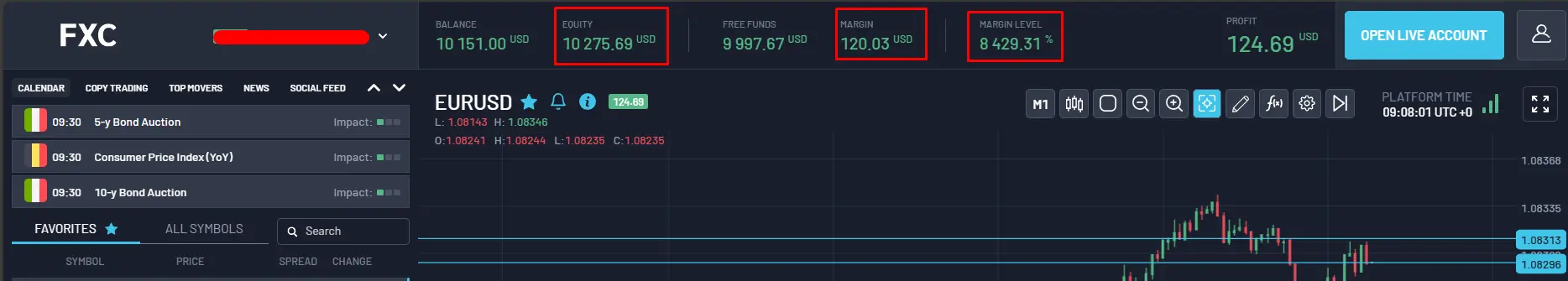
Margin Level on FXC Trader Platform
You do not need to make any calculations concerning the Margin Level, as our platform, FXC Trader, already provides this data. You will be able to see the Equity, Margin, and Margin Level (%).
Understanding Margin Level is not just about knowing a number; it’s about making informed trading decisions, managing risks effectively, and optimizing your strategies. With this knowledge, you’re better equipped to navigate the dynamic world of forex trading. Happy trading, and remember to always trade smart!